برنامه ای بنویسید که موارد زیر را برای CPU و GPU محاسبه کرده و زمان آنها را مقایسه کند:
حسین خسروی
وبلاگ دانشگاهی حسین خسروی، عضو هیات علمی دانشگاه صنعتی شاهرود
طبقه بندی موضوعی
-
برنامه نویسی C
(۱۹)-
مثالهای C
(۹) -
تمرینهای C
(۸) -
اسلایدهای C
(۱)
-
-
شبکه های عصبی
(۹) -
سیستم های چند پردازنده ای
(۷)-
مثالهای MultiCore
(۳) -
تمرینهای MultiCore
(۴)
-
-
بینایی ماشین
(۱۱) -
برنامه ریزی دروس
(۱) -
عمومی
(۱) -
برنامه نویسی پیشرفته
(۱۰)-
مثالهای ++C
(۲) -
تمرینهای ++C
(۷)
-
-
ریزپردازنده
(۸) -
متفرقه
(۶)
پیوندها
کلمات کلیدی
تمرین برنامه نویسی C
تمرین شبکه عصبی
c homework
تمرین OpenCL
OpenCL Programming
C Programming Example
مثال زبان C
ساختار در زبان C
c programming homework
برنامه نویسی OpenCL
مبانی برنامه نویسی
برنامه نویسی
دهمین کنفرانس بینایی ماشین و پردازش تصویر
تمرین بینایی ماشین
تمرین C++
میکرو کنترلر
برنامه نویسی پیشرفته
نحوه استفاده از OpenCV در ویندوز
نوشتن ساختار در فایل باینری
writing structure to binary file
structure
تفاوت فایل متنی و فایل باینری
convolution
Multicore homework
GPU
مرتب سازی حبابی
bubble sort
Neural Networks
Neural Network Homework
مثال سیستم های چند پردازنده
بایگانی
- آبان ۱۴۰۳ (۱)
- مهر ۱۴۰۳ (۴)
- شهریور ۱۴۰۳ (۱)
- آذر ۱۳۹۶ (۱)
- آبان ۱۳۹۶ (۶)
- مهر ۱۳۹۶ (۳)
- شهریور ۱۳۹۶ (۱)
- مرداد ۱۳۹۶ (۱)
- خرداد ۱۳۹۶ (۴)
- ارديبهشت ۱۳۹۶ (۹)
- فروردين ۱۳۹۶ (۲)
- اسفند ۱۳۹۵ (۱۱)
- بهمن ۱۳۹۵ (۳)
- دی ۱۳۹۵ (۲)
- آذر ۱۳۹۵ (۱۱)
- آبان ۱۳۹۵ (۸)
- مهر ۱۳۹۵ (۹)
آخرین مطالب
-
۰۳/۰۷/۲۵فناوری هوش مصنوعی : دوست یا دشمن؟
پیوندهای روزانه
3-1 ضرب نقطه ای دو بردار
مثال شماره 2 درس چند پردازنده
این مثال و برخی از مثالهایی که در جلسات آینده طرح خواهد شد، از مثالهای شرکت AMD است که با تغییراتی در این درس طرح می شوند.
چاپ پیام Hello World از طریق کرنل - فایل CPP که در سمت میزبان اجرا می شود
/********************************************************************** MultiCore Programming Hossein Khosravi Shahrood University of Technology ********************************************************************/ // For clarity,error checking has been omitted. #include <CL/cl.h> #include <string.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <iostream> #include <string> #include <fstream> #define SUCCESS 0 #define FAILURE 1 using namespace std;
//برای دیدن کد کامل، ادامه مطلب را ببینید
مثال شماره 1 درس چند پردازنده
این مثال و برخی از مثالهایی که در جلسات آینده طرح خواهد شد، از مثالهای شرکت AMD است که با تغییراتی در این درس طرح می شوند.
دریافت اطلاعات پردازنده ها
// MultiCore Programming // Hossein Khosravi // Shahrood University of Technology #include "stdafx.h" // You might need to change this header based on your install: #include <CL/cl.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #pragma comment(lib, "OpenCl.lib") static void check_error(cl_int error, char* name) { if (error != CL_SUCCESS) { fprintf(stderr, "Non-successful return code %d for %s. Exiting.\n", error, name); exit(1); } } int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) { cl_uint i; cl_int err; // Discover the number of platforms: cl_uint nplatforms; err = clGetPlatformIDs(0, NULL, &nplatforms); check_error(err, "clGetPlatformIds"); // Now ask OpenCL for the platform IDs: cl_platform_id* platforms = (cl_platform_id*)malloc(sizeof(cl_platform_id) * nplatforms); err = clGetPlatformIDs(nplatforms, platforms, NULL); check_error(err, "clGetPlatformIds"); // Ask OpenCL about each platform to understand the problem: char name[128]; char vendor[128]; char version[128]; fprintf(stdout, "OpenCL reports %d platforms.", nplatforms); cl_device_id devs[3]; for (i = 0; i < nplatforms; i++) { err |= clGetPlatformInfo(platforms[i], CL_PLATFORM_VENDOR, 128, vendor, NULL); err |= clGetPlatformInfo(platforms[i], CL_PLATFORM_NAME, 128, name, NULL); err |= clGetPlatformInfo(platforms[i], CL_PLATFORM_VERSION, 128, version, NULL); check_error(err, "clGetPlatformInfo"); fprintf(stdout, "\n********************\nPlatform %d: %s %s %s\n", i, vendor, name, version); cl_uint num_devices = 0; //find number of devices for each platform //status = clGetDeviceIDs(platform, CL_DEVICE_TYPE_GPU, 0, NULL, &numDevices); err = clGetDeviceIDs(platforms[i], CL_DEVICE_TYPE_ALL, 0, NULL, &num_devices); check_error(err, "clGetDeviceIDs"); cl_device_id* devices = (cl_device_id*) malloc(sizeof(cl_device_id) * num_devices); clGetDeviceIDs(platforms[i], CL_DEVICE_TYPE_ALL, num_devices, devices, NULL); for (int j = 0; j < num_devices; j++) { int maxComputeUnits = 0; // print parallel compute units clGetDeviceInfo(devices[j], CL_DEVICE_MAX_COMPUTE_UNITS, sizeof(maxComputeUnits), &maxComputeUnits, NULL); printf("\n\tNum of compute units: %d\n", maxComputeUnits); cl_uint addr_data = 0; char name_data[100] = { 0 }, ext_data[4096] = { 0 }, version[100] = {0}; err = clGetDeviceInfo(devices[j], CL_DEVICE_NAME, sizeof(name_data), name_data, NULL); err |= clGetDeviceInfo(devices[j], CL_DEVICE_VERSION, sizeof(version), version, NULL); err |= clGetDeviceInfo(devices[j], CL_DEVICE_ADDRESS_BITS, sizeof(addr_data), &addr_data, NULL); err |= clGetDeviceInfo(devices[j], CL_DEVICE_EXTENSIONS, sizeof(ext_data), ext_data, NULL); check_error(err, "clGetDeviceInfo"); printf("\tDevice #%d) NAME: %s\n\tVERSION: %s\n\tADDRESS_WIDTH: %u\n\tEXTENSIONS: %s\n\t----------\n", j, name_data, version, addr_data, ext_data); } free(devices); } getchar(); free(platforms); return 0; }
برای دیدن خروجی، ادامه مطلب را ببینید:
برنامه نویسی - مثال کار با رشته ها
۲۶
مهر۹۵
مثال مطرح شده در کلاس برای کار با رشته ها:
#include <stdlib.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> using namespace std; int main() { //khosravi.blog.ir char s1[20] = ""; char s2[20] = ""; char s3[40] = ""; printf("\nPlease enter 2 strings less than 20 characters\n"); scanf("%s", s1); scanf("%s", s2); if(strcmp(s1, s2) == 0) printf("\nTwo strings are equal"); else printf("\nTwo strings are not equal"); strcpy(s3, s1); strcat(s3, " "); strcat(s3, s2); printf("\ns3 = %s", s3); getchar(); return 0; }
برنامه نویسی - تمرین سری اول
۱۸
مهر۹۵
تمرین سری اول برنامه نویسی
برای دریافت عدد از کاربر از scanf استفاده کنید:
برای چاپ نتیجه از printf استفاده کنید:
2. به پوشه پروژه هایی که ایجاد کرده اید رفته و فایلهای با پسوند *.c, *.cpp, *.h, *.vcxproj (*.cbp) را در پوشه ای با نام خودتان (مثلا HosseinKhosravi) کپی کرده و zip کنید. (فایل exe را نفرستید)
اگر موارد فوق رعایت شود فایل zip شده باید حجمی کمتر از 200 کیلوبایت داشته باشد. این فایل را به آدرس استاد حل تمرین بفرستید.
1. برنامه ماشین حساب ساده (4 عمل اصلی)
برنامه ای بنویسید که 2 عدد اعشاری از کاربر دریافت کرده و چهار عمل اصلی را روی آنها انجام دهد.برای دریافت عدد از کاربر از scanf استفاده کنید:
float n1; printf("Please enter a number: "); scanf("%g", &n1);
printf("Sum of n1 and n2 is %g", n1+n2);
از عبارت کنترلی g% یا f% برای خواندن یا نمایش اعداد اعشاری با دقت معمولی (float) استفاده می شود و از lf% برای اعداد اعشاری دقت مضاعف (double) استفاده می شود.
2. تبدیل رشته به حروف بزرگ و کوچک
برنامه ای بنویسید که یک رشته دریافت کند و حروف کوچک آن را به حروف بزرگ تبدیل کرده و نمایش دهد.3. برنامه معکوس کردن یک عدد 3 رقمی
برنامه ای بنویسید که یک عدد سه رقمی (مثلا 786) دریافت کند و معکوس آن را (687) حساب کرده و نمایش دهد.4. برنامه محاسبه ب.م.م. و ک.م.م
برنامه ای بنویسید که 2 عدد صحیح از کاربر دریافت کرده و ب.م.م و ک.م.م. آنها را حساب کرده و نمایش دهد.روش ارسال تمرینها:
1. یک فایل ورد ایجاد کنید و در صفحه اول مشخصات خودتان و شماره تمرین را ذکر کنید. سپس از اجرای برنامه تان با print screen عکس بگیرید و در همان فایل ورد کپی کنید.2. به پوشه پروژه هایی که ایجاد کرده اید رفته و فایلهای با پسوند *.c, *.cpp, *.h, *.vcxproj (*.cbp) را در پوشه ای با نام خودتان (مثلا HosseinKhosravi) کپی کرده و zip کنید. (فایل exe را نفرستید)
اگر موارد فوق رعایت شود فایل zip شده باید حجمی کمتر از 200 کیلوبایت داشته باشد. این فایل را به آدرس استاد حل تمرین بفرستید.
موعد تحویل 27 مهرماه
برنامه نویسی - تمرین سری صفرم
۱۸
مهر۹۵
تمرین سری صفرم برنامه نویسی
در زبان C اندیسها از صفر شروع می شوند!برای سه مسئله زیر، فلوچارت ترسیم کنید.
1. الف) چگونه مقادیر دو متغیر a و b را با هم جابجا می کنید؟ ب) بدون استفاده از حافظه کمکی اینکار را انجام دهید.
2. چهار متغیر (a,b,c,d) داده شده اند. مقادیر این متغیر ها را به صورت (b,c,d,a) تغییر دهید. یعنی:
- مقدار جدید a برابر با مقدار قبلی b باشد
- مقدار جدید b برابر با مقدار قبلی c باشد
- مقدار جدید c برابر با مقدار قبلی d باشد
- مقدار جدید d برابر با مقدار قبلی a باشد
3. فلوچارت یافتن تعداد ارقام یک عدد صحیح را ترسیم کنید. مثلا اگر عدد 52489657 به عنوان ورودی داده شود، باید عدد 8 به عنوان خروجی تحویل داده شود.
این تمرین را روی کاغذ انجام داده و تحویل استاد حل تمرین، خانم علوی دهید.
موعد تحویل 27 مهرماه
مثالهای ساده از برنامه نویسی C
۱۸
مهر۹۵
اولین گام در هر موضوع جدیدی، معمولا سخت ترین گام است و گامهای بعدی با توجه به اینکه ترس ما از موضوع ریخته است، دشواری ندارد.
برای شروع برنامه نویسی C، چند مثال از مثالهای که در کلاس مطرح شد، در اینجا قرار می دهم که روی رایانه خودتان تست کنید و برای نوشتن تمرینها آمادگی داشته باشید:
مثال 1: برنامه سلام دنیا
خروجی مثال سلام دنیا
مثال 2: بررسی زوج و فرد بودن عدد ورودی
خروجی مثال زوج و فرد
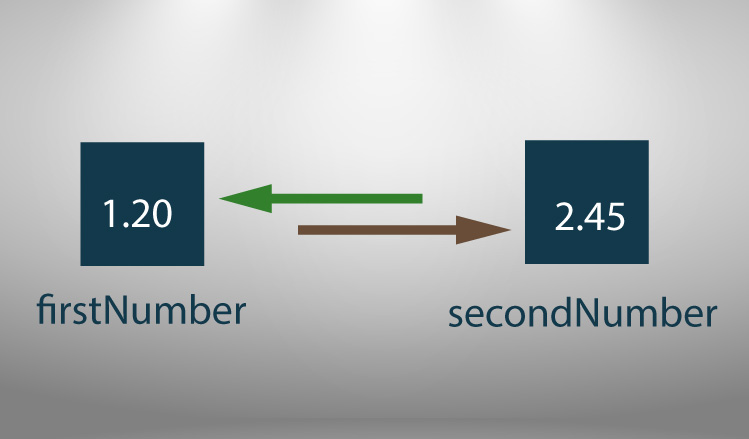
خروجی مثال جابجایی دو عدد
برای شروع برنامه نویسی C، چند مثال از مثالهای که در کلاس مطرح شد، در اینجا قرار می دهم که روی رایانه خودتان تست کنید و برای نوشتن تمرینها آمادگی داشته باشید:
مثال 1: برنامه سلام دنیا
#include <stdio.h> int main() { // printf() displays the string inside quotation printf("Hello, World!"); return 0; }
خروجی مثال سلام دنیا
Hello, World!
مثال 2: بررسی زوج و فرد بودن عدد ورودی
#include <stdio.h> int main() { int number; printf("Enter an integer: "); scanf("%d", &number); // True if the number is perfectly divisible by 2 if(number % 2 == 0) printf("%d is even.", number); else printf("%d is odd.", number); return 0; }
خروجی مثال زوج و فرد
Enter an integer: -7 -7 is odd.
مثال 3: جابجا کردن مقدار دو متغیر با استفاده از متغیر کمکی
توضیح: این مثال برای جابجایی دو عدد اعشاری (double) نوشته شده است. برای دریافت اعداد اعشاری از lf% استفاده می کنیم. اگر بخواهید برنامه را برای اعداد صحیح بنویسید، به جای double از int و به جای lf% از d% استفاده کنید.

#include <stdio.h> int main() { double firstNumber, secondNumber, temporaryVariable; printf("Enter first number: "); scanf("%lf", &firstNumber); printf("Enter second number: "); scanf("%lf",&secondNumber); // Value of firstNumber is assigned to temporaryVariable temporaryVariable = firstNumber; // Value of secondNumber is assigned to firstNumber firstNumber = secondNumber; // Value of temporaryVariable (which contains the initial value of firstNumber) is assigned to secondNumber secondNumber = temporaryVariable; printf("\nAfter swapping, firstNumber = %.2lf\n", firstNumber); printf("After swapping, secondNumber = %.2lf", secondNumber); return 0; }
خروجی مثال جابجایی دو عدد
Enter first number: 1.20 Enter second number: 2.45 After swapping, firstNumber = 2.45 After swapping, secondNumber = 1.20مثالها از سایت مثالهای C برداشته شده است و می توانید مثالهای بیشتری را آنجا مطالعه کنید.
اسلایدهای شبکه عصبی
۱۶
مهر۹۵
سری اول اسلایدهای درس برنامه نویسی C
۱۲
مهر۹۵
